Improved Reporting and Risk Management Under Solvency II
Written by Mads Raunholt-Jensen, Manager | The 6th of May 2021
With the RegTech DataHub’s Solvency II data and the solvency hierarchy module, CMP has developed a software solution targeted towards the insurance and pension sector, which makes it easy to report LEI codes and ultimate parent LEI codes for all investments.
More importantly, the solution provides the correct data for an automated daily calculation of the concentration and counterparty risk within the Solvency II standard model, using ultimate parent LEI codes as a single name exposure aggregation key.
In the following article we will explain our solution and the opportunities it offers.
COVID-19 and Extraordinary Reporting
Most Danish pension and insurance companies have come a long way with data management, calculations and reporting since Solvency II came into force in 2016. However, the Danish FSA’s requirements for extraordinary reporting in connection with the COVID-19 market volatility has shown, that there is still a need for data optimization in order for Solvency Capital Requirement (SCR) calculations to be carried out more frequently and on a more accurate basis.
The Solvency II Standard Model
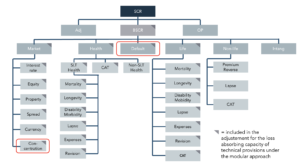
The first pillar of the Solvency II regulation requires all European insurance and pension companies to always hold sufficient capital to cover the financial loss occurring in a 200-year event or with a probability equal to the 99.5% percentile. This financial loss is expressed by the SCR – see Figure 1 below.
The standard model is essential for consumer protection for policyholders and pension savers, and it directly determines the asset allocation of companies and thus the pricing of assets in the market.
Figure 1 shows the modular framework of the standard model:
The risk categories Concentration and Default are highlighted, and the following explains how to improve and simplify the data management of these two risk categories.
Concentration and Default Risk on a Daily Basis
In order to determine the concentration risk and counterparty risk according to the standard model, there is a need to know each separate exposure and the total exposure stemming from issues belonging to the same group company. The group company exposure is called the ultimate parent exposure or the single name exposure.
Until recently, a unique aggregation key to perform these calculations simply has not been available. However, with the improved data quality and volume of LEI codes, this has become possible.
The tricky part remaining, is for each ISIN code to have full control over the relation between the direct issuer LEI code, as well as the ultimate parent LEI code. If the calculations are to be automated and carried out daily, then this data must be in place.
With hundreds or thousands of investments, and with investments in companies with deep ownership structures, it is not a trivial task automatically to find the way from single investments to the LEI code of the direct issuer, and finally to the LEI code of the ultimate parent issuer.
The RegTech DataHub’s Solvency hierarchy module carries out exactly this task in an instant, and subsequently makes it easy to integrate with existing systems either by file exchange or API requests.
The illustration below shows the concept in all its simplicity. All that is required is a list of ISIN codes in order for the solvency hierarchy module to return issuer LEI codes and ultimate parent LEI codes.
The entire tree structure
In fact, the module can also return the full ownership tree structure. This can be useful and crucial in cases where the ultimate risk parent is not necessarily the top node in the ownership tree.
LEI and CIC for QRT Reporting
In addition to the SCR calculations, since January 1st, 2016 it has been mandatory for insurance and pension companies to carry out quarterly and yearly quantitative reporting templates reporting (QRTs).
Although the QRTs are only to be reported quarterly under normal circumstances, EIOPA’s requirements for schema validation are constantly tightened. Insufficient data quality therefore prevents the QRTs to be approved for final reporting. This in turn, creates an ineffective and recurring resource consumption every quarter.
QRT s.06.02 and s.06.08 and look-through QRT s.06.03
In QRT s.06.02 and s.08.02, all securities and derivatives must be reported with LEI codes and legal names and ultimate parent LEI codes and legal names among others.
QRT s.06.03 contains information on the look through of collective investment undertakings or investments packaged as funds, by underlying asset category according to the 3. CIC character, country of issue and currency.
Having different external fund investments, this template can be troublesome for the reporting companies.
The RegTech DataHub’s SII data solution automatically returns all values to s.06.03.
The RegTech DataHub’s Solvency II Solution
The RegTech DataHub is structured as a series of modules that are tailor-made for the specific customer and authority reporting needs for both banking, insurance and pension sectors. The modular structure ensures that our clients get the simplest and most appropriate solutions for their exact purpose, and accordingly only pay for the data they need.
The RegTech DataHub’s different modules are shown below. The Solvency II module is highlighted in the figure.
The Solvency hierarchy module
Based on ISIN codes, this module returns LEI codes and ultimate parent LEI codes as well as the tree structure of LEI codes throughout the issuer hierarchy up to the ultimate parent issuer LEI code.
Based on ISIN codes, the module delivers:
- LEI codes and associated legal name
- Ultimate parent LEI codes and associated legal name
- CIC for s.06.03
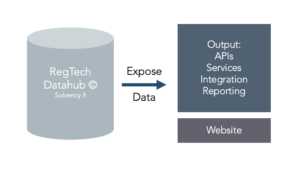
Data Output
Output can be delivered in different ways depending on customer needs. This can be txt-, csv-, xml files or full integration solutions as well as API queries.
In addition, there is a website solution where data can be looked up and readily presented for ad hoc purposes.
ABOUT CMP:
Our name, Capital Market Partners, reflects what we define as our core service: Business understanding based on extensive experience in applying technology in the capital market area.
As a business partner, we offer consulting services based on our combination of business understanding and IT know-how. Our work with analyzes, implementation of IT systems and other projects supports strategic decisions at different levels in complex business contexts.
For further information – Please contact:
Lars Christiansen
Managing Partner
Tel: +45 2993 4678